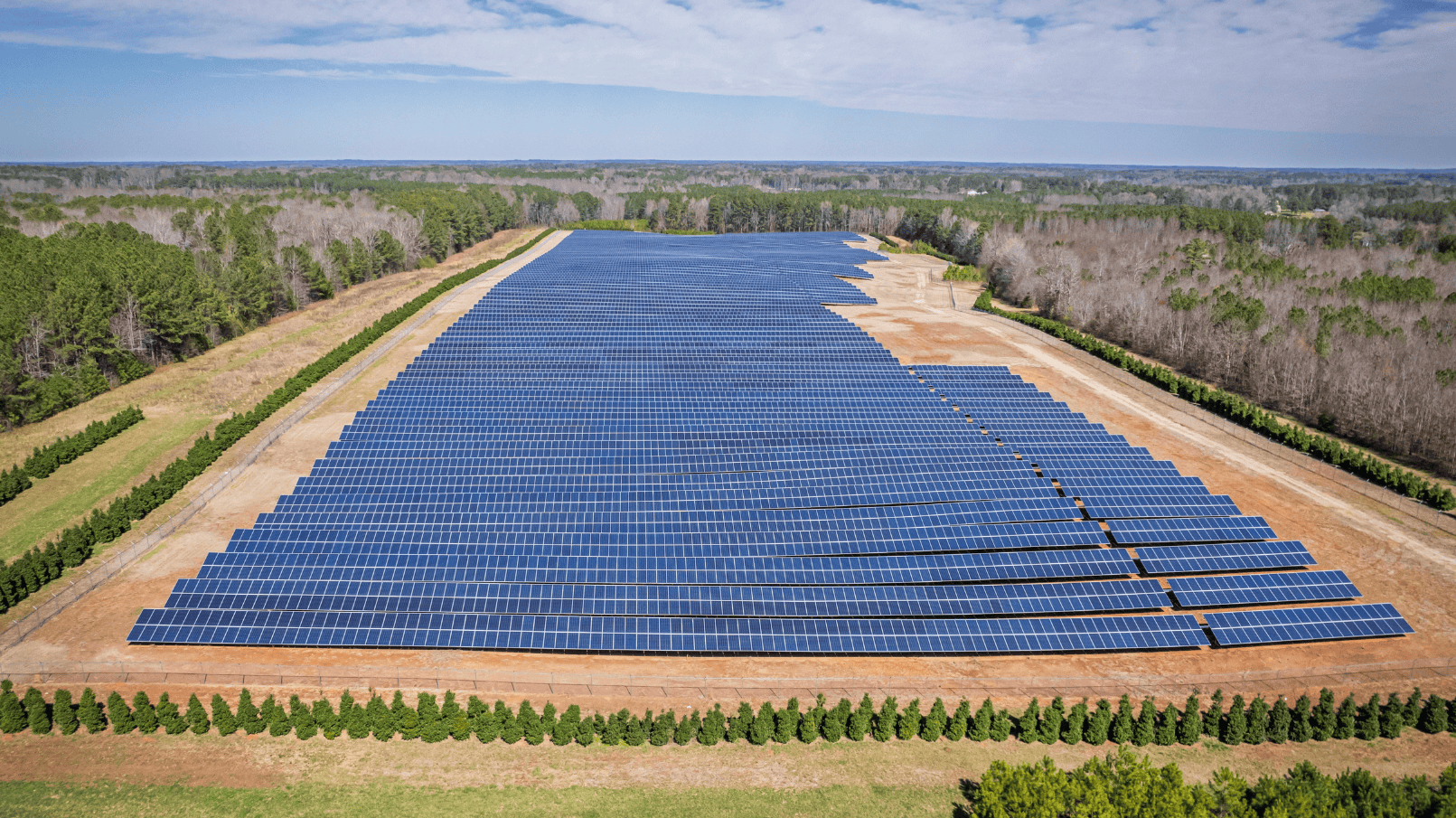
Leasing land for solar project development is an attractive opportunity for landowners; however, solar land leasing involves more than just signing a contract. It requires navigating complex legal considerations of solar land leasing to ensure compliance with zoning laws, environmental regulations, and lease agreements. Understanding the legal landscape of solar land leasing helps landowners avoid common pitfalls, mitigate risks, and establish successful, long-term partnerships. This article breaks down the essential legal compliance aspects of leasing land for renewable energy, including contract terms, permitting requirements, community concerns, and best practices for legal protection.
Legal Considerations Of Solar Land Leasing
There are many legal nuances to consider when leasing your property for a solar project. Some of the more important considerations include:
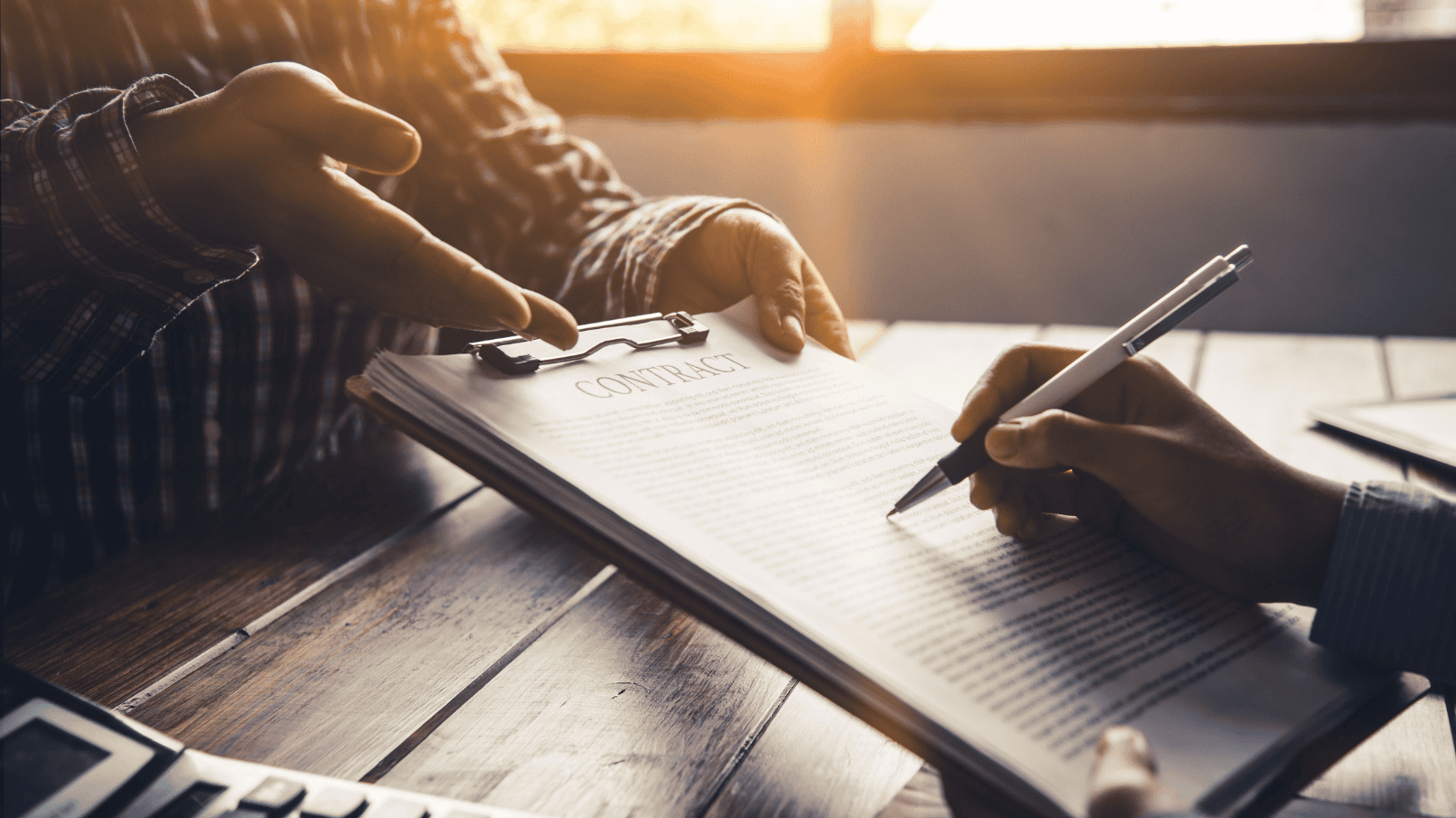
1. Understanding Solar Lease Agreements
A solar lease agreement outlines the rights and responsibilities of both the landowner and the solar developer. Key contractual elements include:
- Lease Term & Payment Structure: Most solar land leases last 20–30 years, with payments structured as fixed annual rates per acre or revenue-sharing models. It’s critical to consider the lease length to ensure it matches the lifespan of the solar project.
- Land Use & Restrictions: This defines how the land can be used during the lease, including farming or grazing alongside the solar panel system. Some leases restrict land use and can be detrimental for farmers looking to continue using the land during the solar term.
- Liability & Insurance: This specifies who is responsible for property damages, accidents, and insurance coverage. It’s important that your contract clearly spells out roles and responsibilities and your recourse if the solar developer is in default.
- Decommissioning & Restoration: This section outlines the process for solar panel removal and returning the land to its original state at the end of the lease. Choosing a reputable solar developer that will be in business for the term of the lease is critical so you do not have to hire another company to decommission the solar panels on your property.
2. Legal Compliance For Landowners
Landowners must ensure their property meets legal compliance standards before entering a solar lease agreement. This includes:
- Zoning & Permitting Regulations: Local and state authorities determine whether solar project development is permitted on specific land parcels.
- Tax Implications: Leasing land for solar power may impact property tax status and eligibility for agricultural exemptions.
- Environmental Restrictions: Wetlands, endangered species habitats, and protected lands may restrict solar panel installation.
3. Community Considerations
Communities play a critical role in shaping the legal landscape of solar land leasing. Common objections to solar include:
- Aesthetic & Noise Impact: Residents may worry about the visual impact of solar farms and construction traffic during the development of the system.
- Economic Benefits: Local governments may offer tax incentives or demand community engagement in solar energy projects.
- Public Opposition: Some communities resist solar project development due to misinformation about solar farms.
4. Legal Responsibilities Of Solar Developers
A solar developer must navigate a complex regulatory framework to ensure solar project development complies with local, state, and federal laws. This includes:
- Title Review & Site Control: Developers must ensure the land title is clear of encumbrances before proceeding with solar lease agreements. Furthermore, they must have clear site control, allowing them to construct a solar project on the property in order to offer a lease for the land.
- Permitting & Regulatory Approvals: Developers must secure environmental impact assessments and interconnection applications for grid access.
- Risk Management & Liability Mitigation: They must have insurance policies to cover construction, maintenance, and potential environmental impacts.
- Decommissioning & Land Restoration: Developers must guarantee proper removal of the solar panel system at the end of the lease.
Common Pitfalls Of Solar Land Leasing
Even with a well-structured solar land lease, challenges can arise. Common legal pitfalls include:
- Failure To Conduct Proper Due Diligence: Not researching zoning laws or environmental restrictions can delay projects. Solar lease agreements can be delayed if the land is not suitable for solar. In certain cases, the land can be prepared for a solar lease by removing trees, flattening land, and getting local zoning approvals.
- Vague Lease Terms: Agreements without clear exit clauses or payment structures can create disputes between landowners and solar developers. These terms need to be clear to not create conflict upon signing.
- Lack Of Legal Representation: Entering an agreement without legal counsel can lead to unfavorable contract terms for the proptery owner. Landowners should seek legal and financial guidance before signing a solar lease agreement to avoid these risks.
Why Work With An Experienced Solar Developer?
Partnering with a reputable solar partner ensures legal compliance, transparent contracts, and long-term financial security. An experienced solar developer will:
- Ensure regulatory compliance with local zoning laws and permitting requirements.
- Provide clear lease agreements with fair payment structures.
- Manage interconnection applications and ensure proper land restoration at lease termination.
- Navigate the complexities of material procurement, engineering, and construction management.
Why Partner With Us
Genie Solar Energy is a trusted leader in solar project development, helping landowners navigate the legal landscape of solar land leasing. Our team ensures transparent lease agreements, full regulatory compliance, and competitive lease rates up to $5,000 per acre. If you’re considering leasing your land for a solar farm, contact our team of solar leasing experts today for expert guidance and a free land assessment.